
Maroons In Suriname / Blog maroonlifeandculture (Maroon Life and culture in 28 In
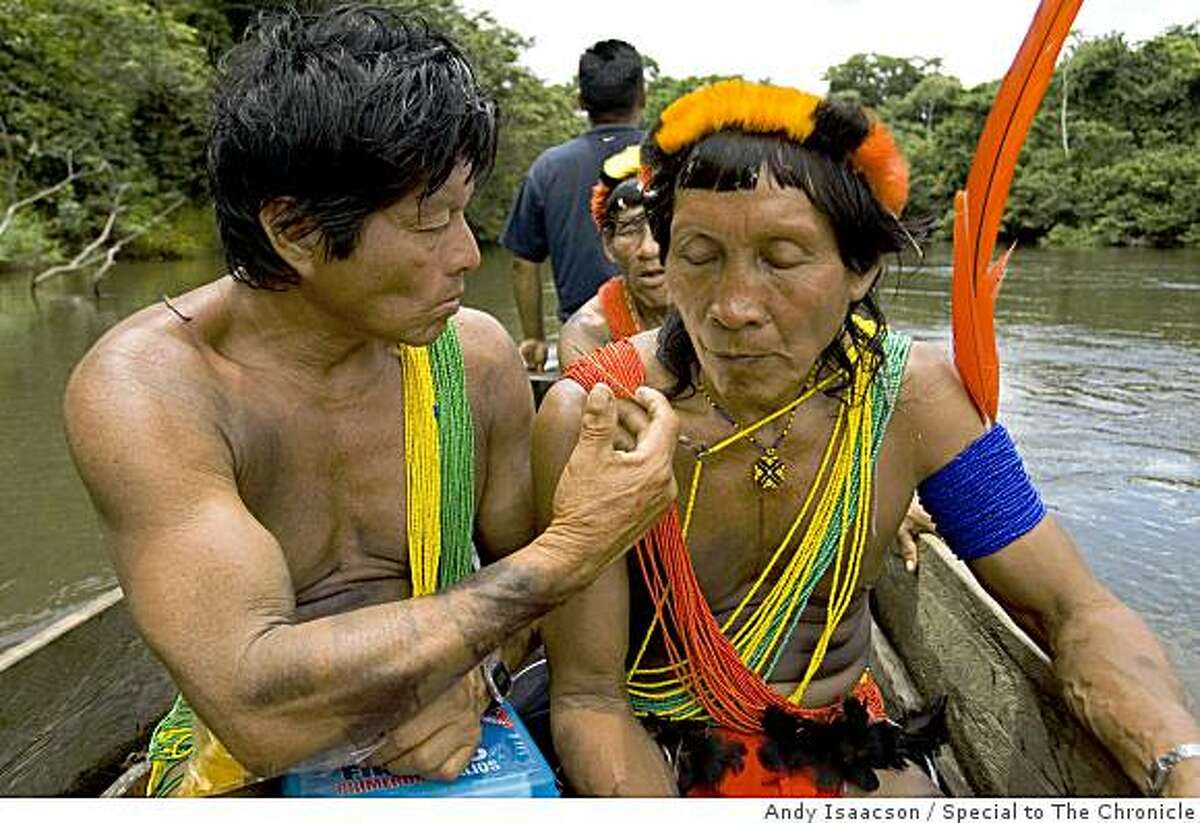
Saramaka The Saramaka, Saamaka or Saramacca [note 1] are one of six Maroon peoples (formerly called "Bush Negroes") in the Republic of Suriname and one of the Maroon peoples in French Guiana.
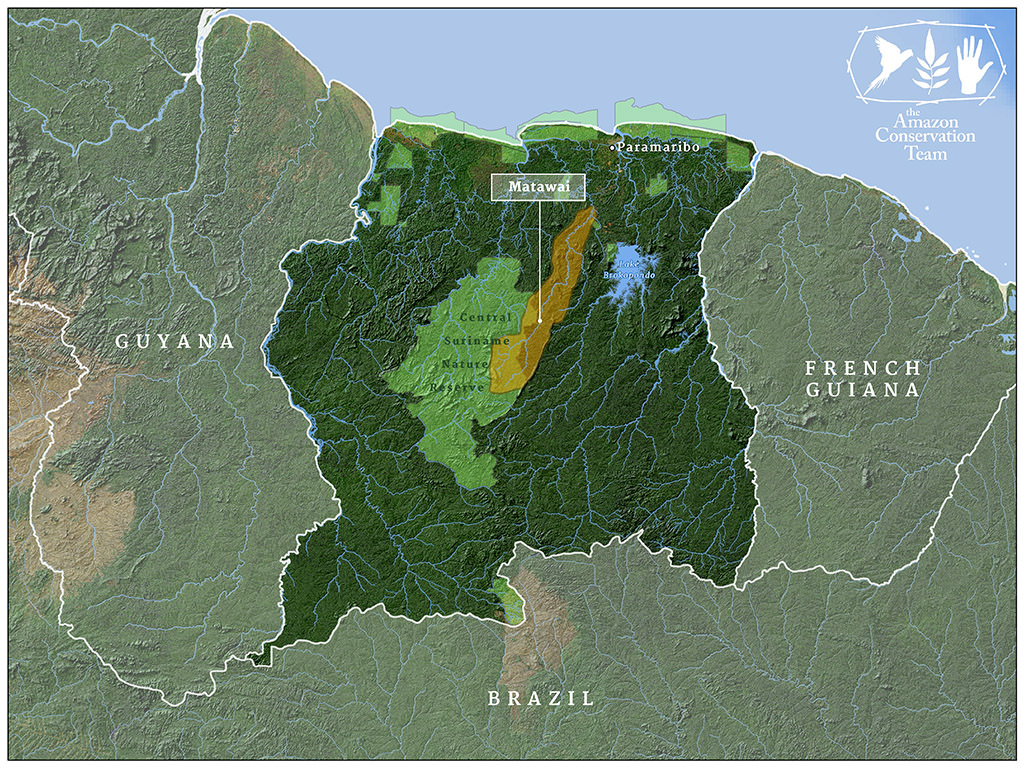
Mapping the traditional lands of the Matawai Maroons in Suriname, one creek at a time Amazon
Indigenous people and Maroons, descendants of Africans in the Americas who formed settlements away from slavery, and often mixed with Indigenous populations, comprise the main tribal groups of Suriname.

Black History Heroes Black Suriname African Maroon Societies in South America
Maroons in the South American rainforest in Suriname and French Guiana continue to battle encroachment by miners and loggers given concessions by the state—including the building of roads that would intersect their traditional hunting grounds and farmlands.

Maroons In Suriname / Blog maroonlifeandculture (Maroon Life and culture in 28 In
Maroon communities in Suriname In the mid-1600s, British, and then Dutch, colonists imported African slaves to work the sugar plantations. Conditions were brutal, and many slaves escaped into the jungle. (The term "maroon," used throughout the New World, is said to come from cimarrón, a Spanish term for runaway slaves.)

Maroons In Suriname Pin van Eersteling Consultancy op SURINAME MAROONS / Marrons in
Suriname Maroons. Slavery and Abolition, 12 (1), 107-127. Riemer, J. A. (1801). Missions-Reise nach Suriname und Barbice zu einer am Surinam-fluss im dritten Grade der Linie wohnenden Freineger-Nation [Mission trip to Suriname and Barbice to a Freineger nation living on the Surinam River in the third degree of the line]. Zittau and Leipzig.

Maroons and Indigenous people in Suriname the struggle for land rights
Indigenous Peoples and Maroons in Suriname Author Kambel, Ellen-Rose Date Sep 2006 English ( 2894 downloads) View Online This study provides a concise analysis of the current challenges facing Indigenous and Maroon communities in Suriname and provides recommendations for possible Bank support.

De Marrons in Suriname overwonnen de kolonisator maar hun strijd gaat door
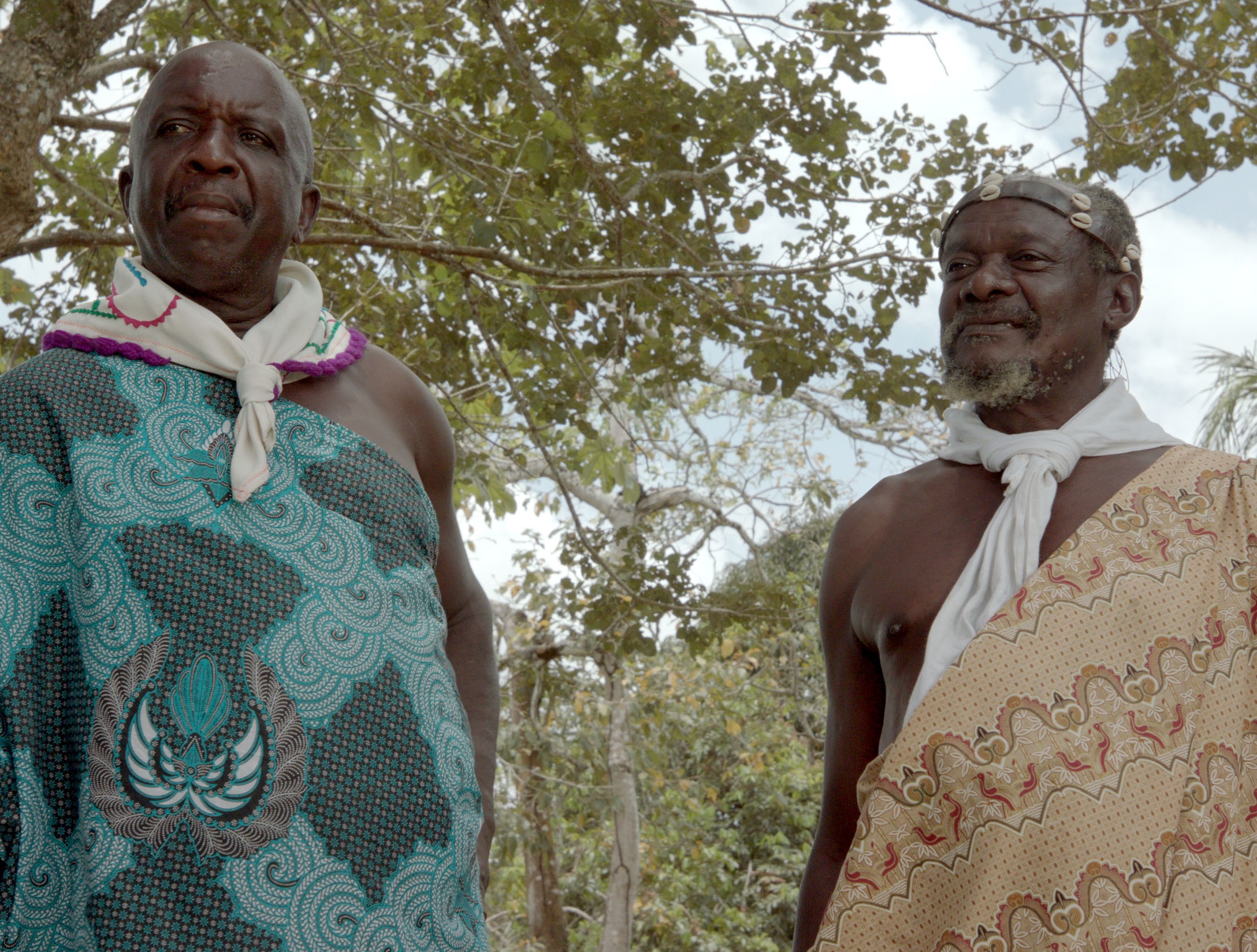
The Maroons of Suriname and French Guiana (formerly known as "Bush Negroes") have long been the hemisphere's largest Maroon population. They are at once the most culturally, politically, and economically independent of all Maroon peoples in the Americas and, since the 1970s and 80s, the most heavily under assault. Historical Origins

Maroons slave hires stock photography and images Alamy
The author is exploring the site of Kumako in Suriname, a destination for Maroons escaping from plantations in coastal Suriname between the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. She finds evidence for a structured settlement, distinctive pottery and local ritual practices, raising new questions about the degree of interaction and acculturation.
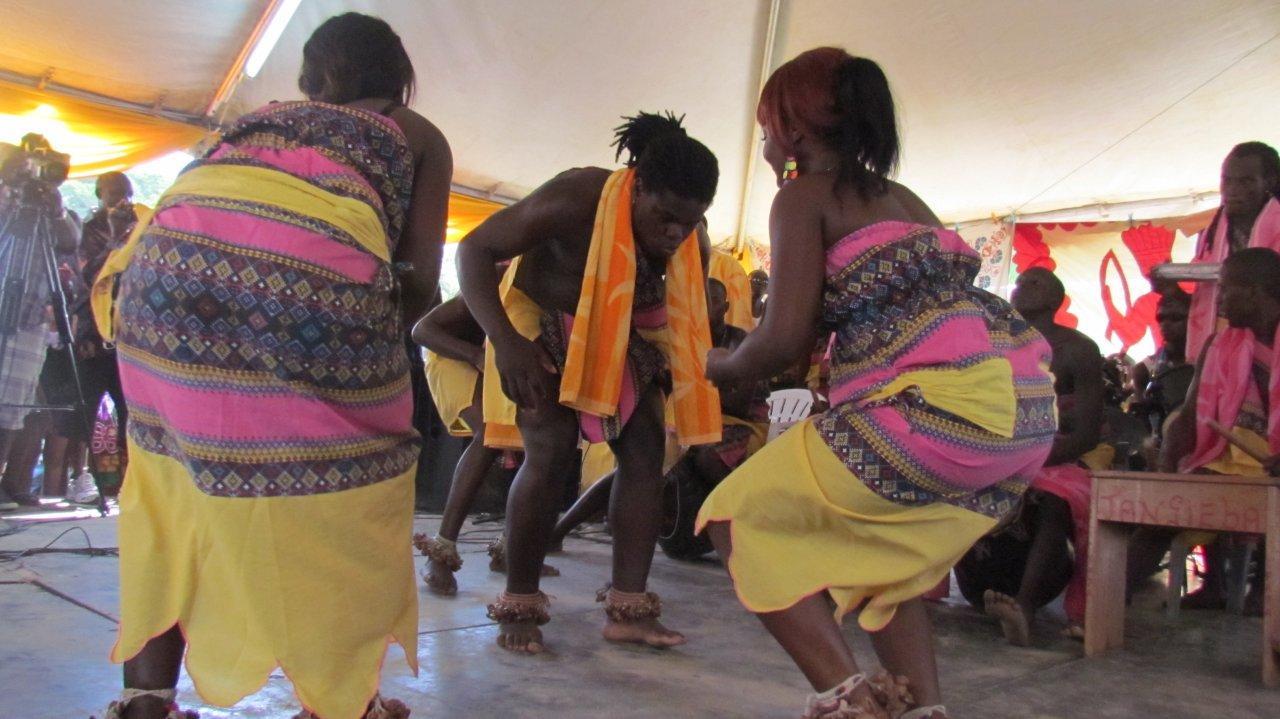

Umoja • Saramaccan Maroons of Suriname performing their...
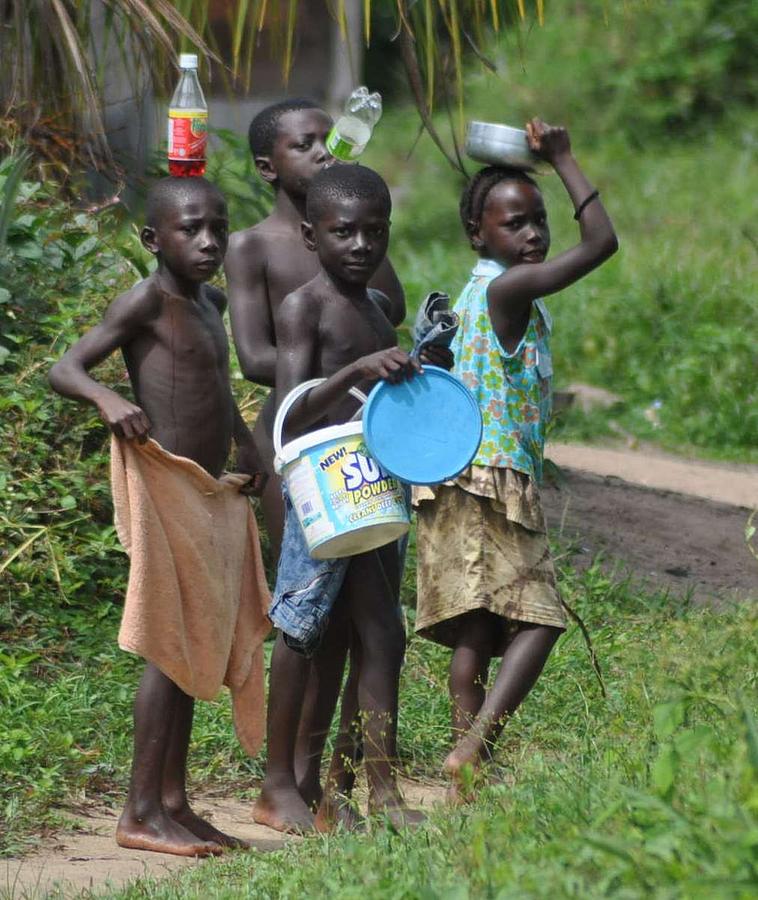
Profile The Maroons are descendants of Africans who fled the colonial Dutch forced labour plantations in Suriname and established independent communities in the interior rainforests. They have retained a distinctive identity based on their West African origins.

Suriname. Maroon musician. South america, Suriname, America
Suriname Maroons. A History of Intrusions into their Territories August 2020 In book: Slavery, Resistance and Abolitions. A Pluralist Perspective (pp.215) Publisher: Africa World Press Authors:.

Maroons In Suriname Maroons And Indigenous People In Suriname The Struggle For Land Rights
Surinamese Maroons (also Marrons, Businenge or Bushinengue, meaning black people of the forest) are the descendants of enslaved Africans that escaped from the plantations and settled in the inland of Suriname (Dutch Guiana). The Surinamese Maroon culture is one of the best-preserved pieces of cultural heritage outside of Africa.
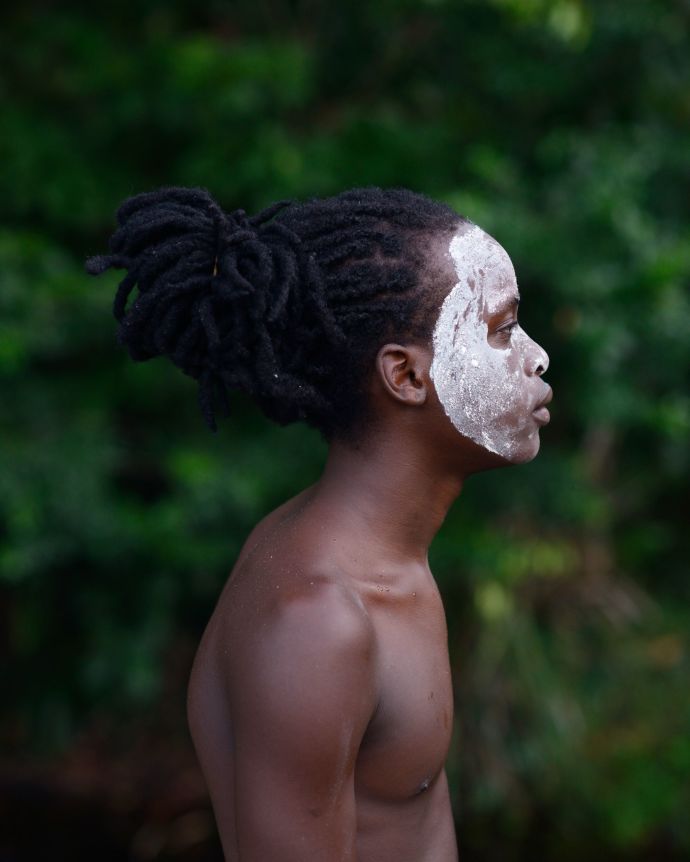

Nicola Lo Calzo Maroons in Suriname and Guiana
The Maroons were descendants of African slaves who managed to escape from the plantations during the colonial era. Instead of succumbing to a life of oppression, they chose to run away and find safety and freedom in the inhospitable interior of Suriname.

Pin on People
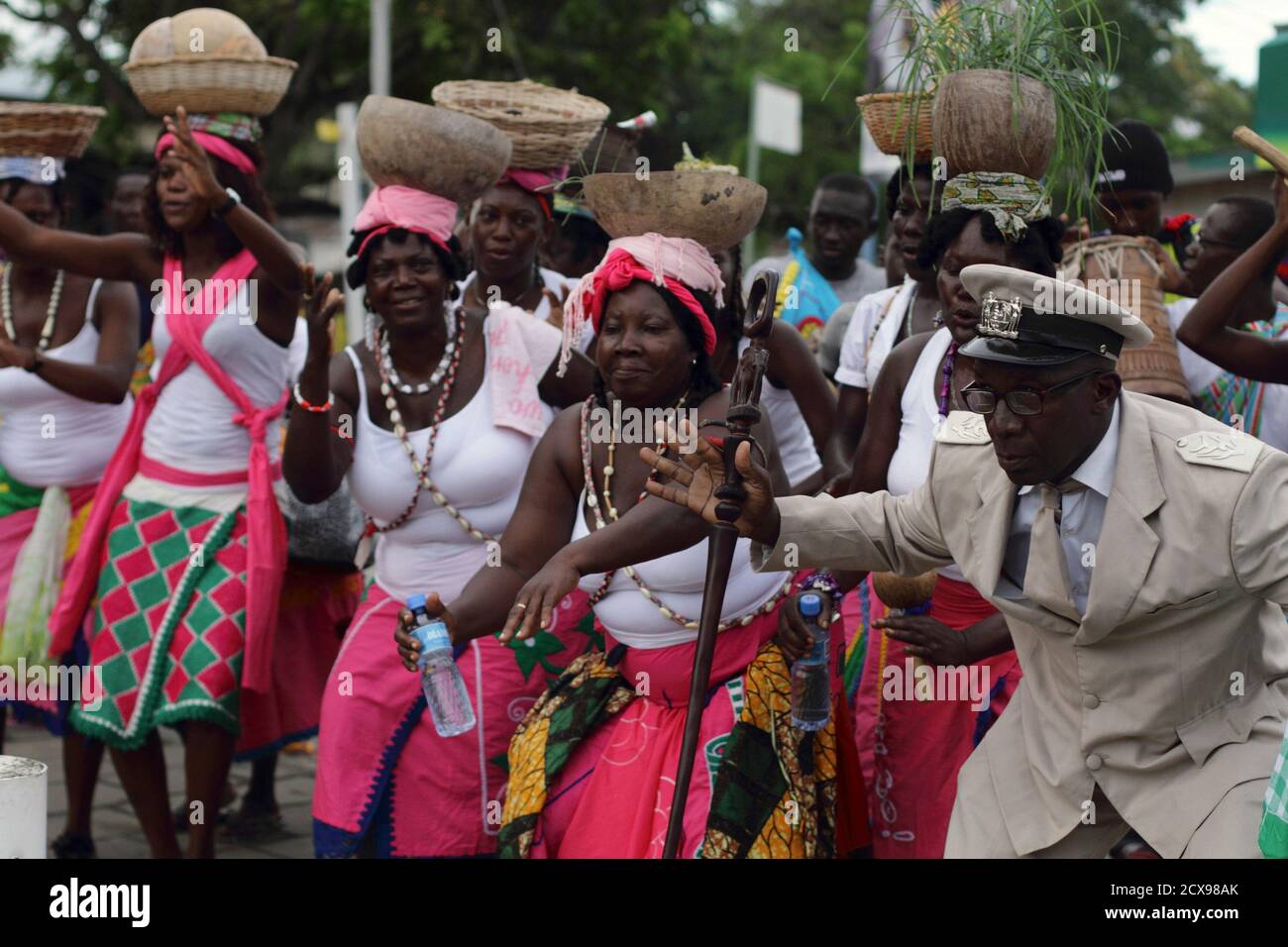
The daily life of Maroons in the interior of Suriname is unusually rich in artistic activity and aesthetic discussion. The anthropologist Melville Herskovits remarked in 1930 (using a term for the Suriname Maroons that was standard in his day): "Bush Negro art in all its ramifications is, in the final analysis, Bush Negro life."

Maroons In Suriname / Blog maroonlifeandculture (Maroon Life and culture in 28 In
Ndyuka man bringing the body of a child before a shaman. Suriname, 1955 Maroons are descendants of Africans in the Americas and Islands of the Indian Ocean who escaped from slavery and formed their own settlements. They often mixed with indigenous peoples, eventually evolving into separate creole cultures [1] such as the Garifuna and the Mascogos .
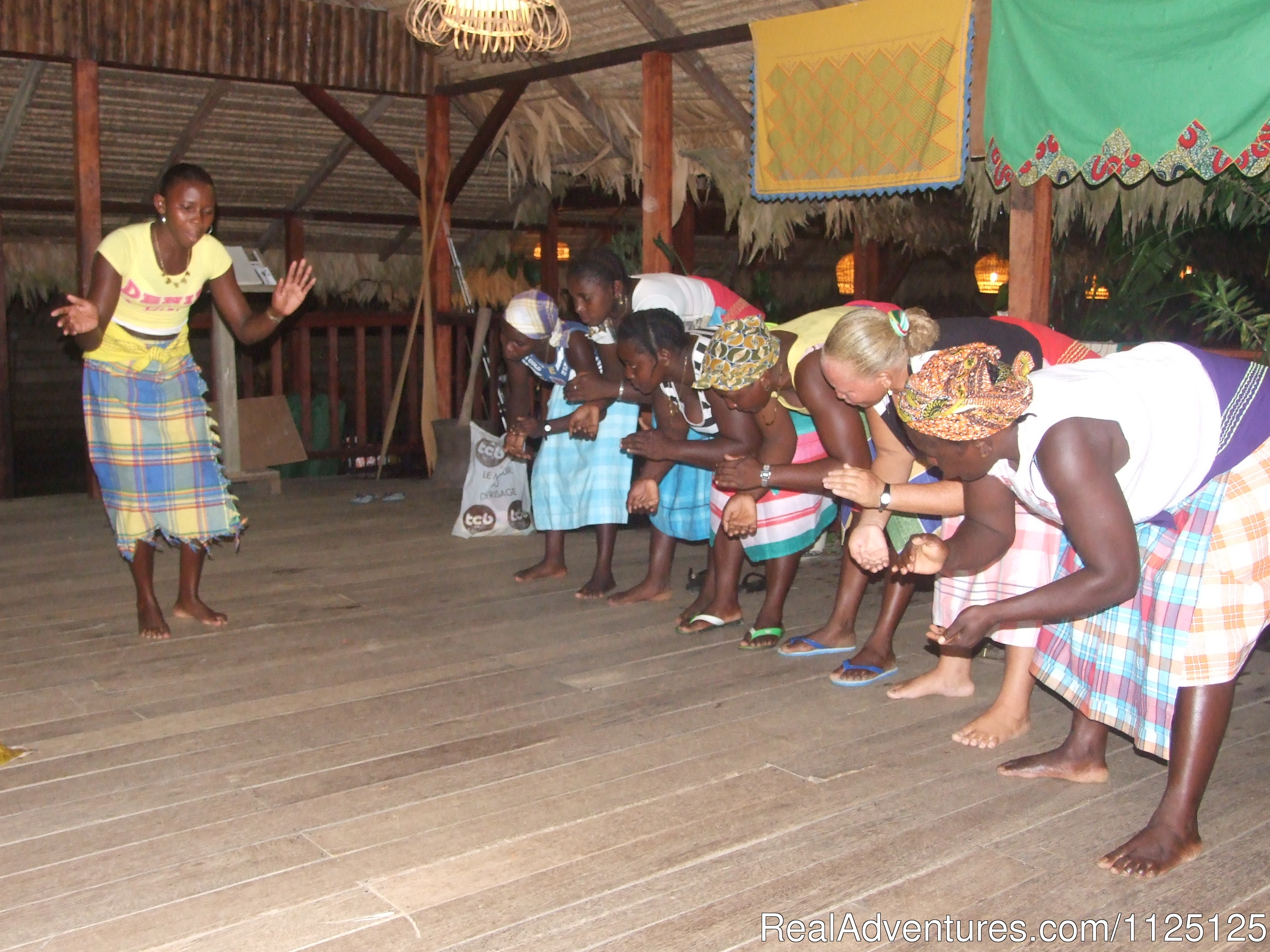

Maroons In Suriname / Blog maroonlifeandculture (Maroon Life and culture in 28 In
Surinamese Maroons are the descendants of enslaved Africans that escaped from the plantations and settled in the inland of Suriname . The Surinamese Maroon culture is one of the best-preserved pieces of cultural heritage outside of Africa. Colonial warfare, land grabs, natural disasters and migration have marked Maroon history. In Suriname six Maroon groups — or tribes — can be.
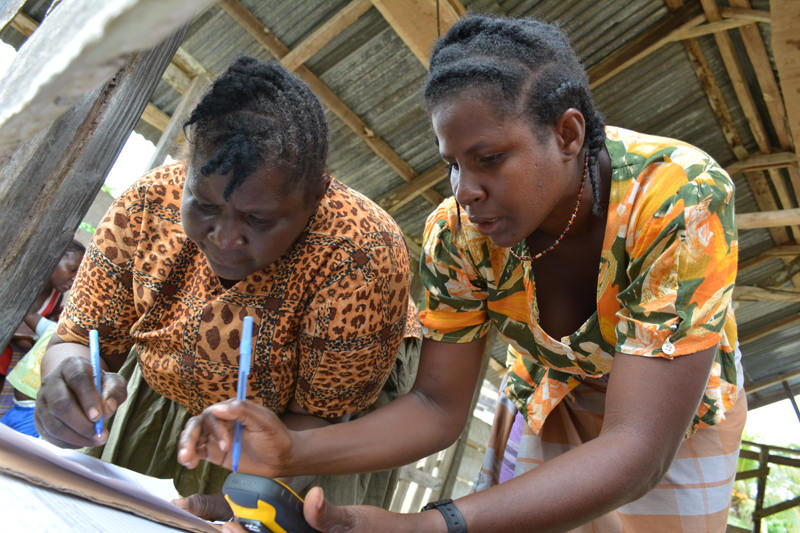

Mapping the traditional lands of the Matawai Maroons in Suriname, one creek at a time Amazon
The Maroons of Suriname thus were among the first people in this hemisphere to gain their independence. Ultimately, they became one of the largest and most concentrated groups of descendants of runaway slaves in the world. The Maroons had enjoyed 100 years of freedom before slavery was finally abolished in 1863. For hundreds of years they were.